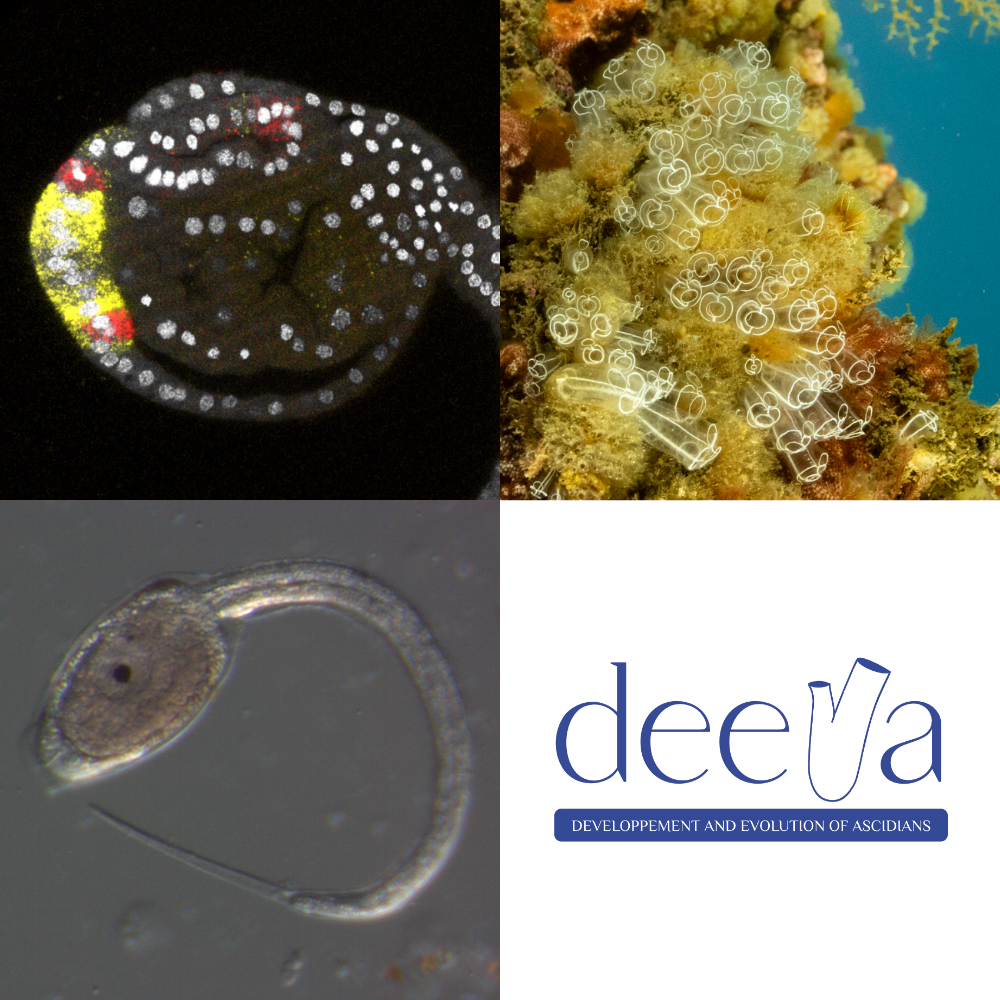
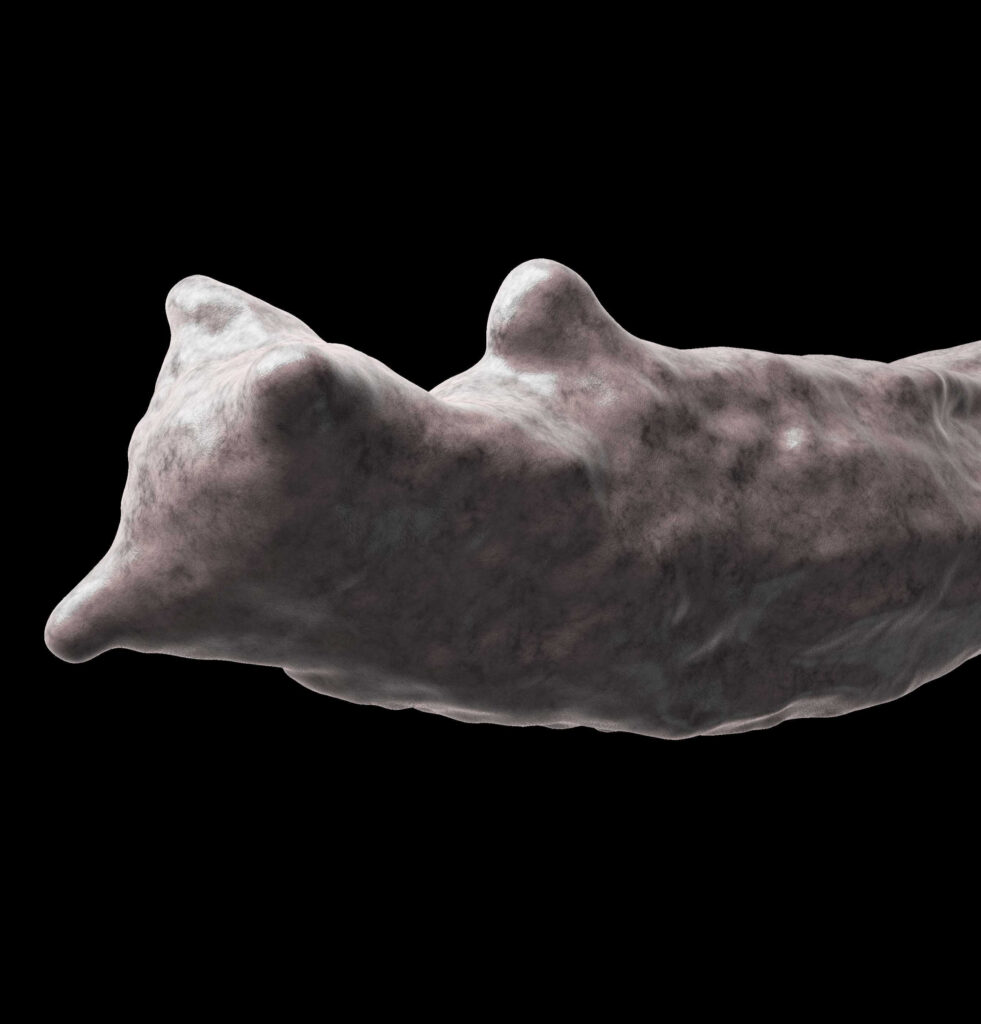
Last publication from the DEEVA team!
The study details how the canonical Wnt signaling patterns the anterior neurectoderm during the development of the ascidian Ciona intestinalis. Although the global biological function is conserved with other animals, the underlying molecular and regulatory logics have significantly changed.
Roure A, Chowdhury R and Darras S (2025). Six3/6 acts downstream of canonical Wnt signaling to regulate the formation of anterior neural border-derived structures in ascidian embryos. Development 152 (23): dev204927. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.204927
In this issue of Development, you can also read a Research Highlight: A palp-able conservation of Wnt signalling in neuroectoderm patterning and an Interview: The people behind the papers – Agnès Roure and Sébastien Darras